Controller overview
Each different hardware object is directly controlled by a software object called controller. This object is responsible for mapping the communication between a set of hardware objects (example motors) and the underlying hardware (example: a motor controller crate). The controller object is also exposed as a Tango device.
Usually a controller is capable of handling several hardware objects. For example, a motor controller crate is capable of controlling several motors (generally called axis [1]).
The controller objects can be created/deleted/renamed dynamically in a running pool.
A specific type of controller needs to be created to handle each specific type of hardware. Therefore, to each type of hardware controller there must be associated a specific controller software component. You can write a specific controller software component (plug-in) that is able to communicate with the specific hardware. You can this way extend the initial pool capabilities to talk to all kinds of different hardware.
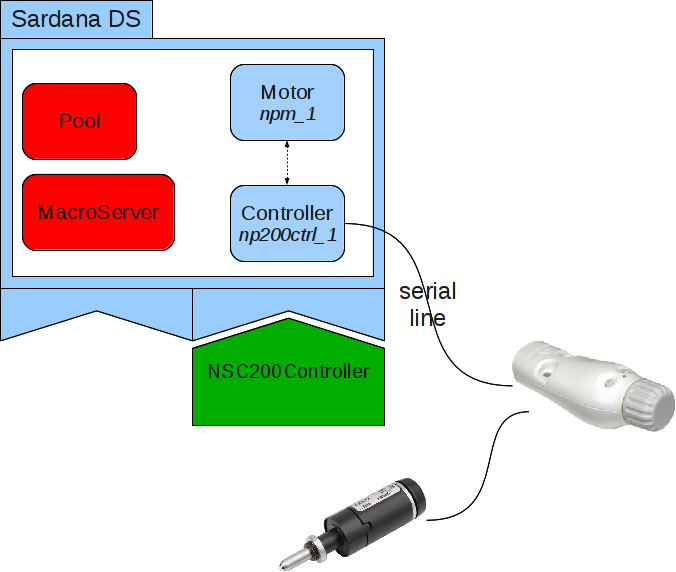
A diagram representing a sardana server with a controller class NSC200Controller, an instance of that controller np200ctrl_1 “connected” to a real hardware and a single motor npm_1.
A sardana controller is responsible for it’s sardana element(s). Example: an Icepap hardware motor controller can control up to 128 individual motor axis. In the same way, the coresponding software motor controller IcepapController will own the individual motor axises.
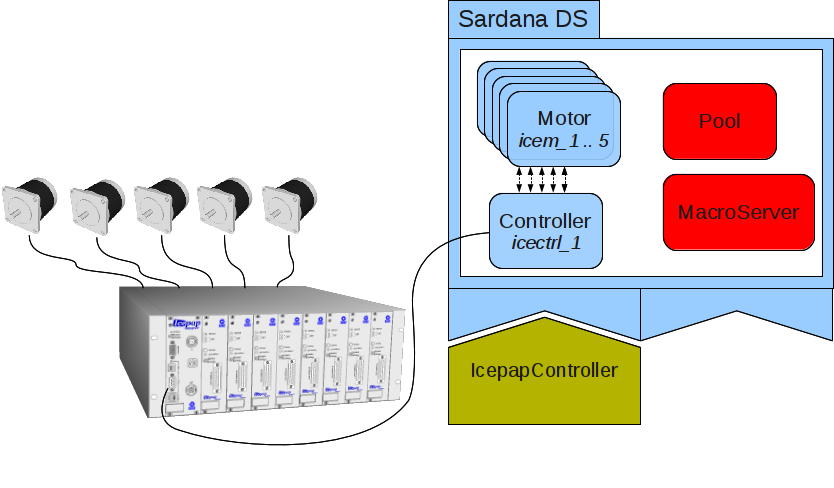
A diagram representing a sardana server with a controller class IcepapController, an instance of that controller icectrl_1 “connected” to a real hardware and motors icem_[1..5].
These are the different types of controllers recognized by sardana:
MotorControllerYou should use/write a
MotorControllersardana plug-in if the the device you want to control has a moveable interface. TheMotorControlleractually fullfils a changeable interface. This means that, for example, a power supply that has a current which you want to ramp could also be implemented as aMotorController.Example: the Newport NSC200 motor controller
CounterTimerControllerThis controller type is designed to control a device capable of counting scalar values (and, optionaly have a timer).
Example: The National Instruments 6602 8-Channel Counter/Timer
ZeroDControllerThis controller type is designed to control a device capable of supplying scalar values. The API provides a way to obtain a value over a certain acquisition time through different algorithms (average, maximum, integration).
Example: an electrometer
OneDControllerThis controller type is designed to control a device capable of supplying 1D values. It has a very similar API to
CounterTimerControllerExample: an MCA
TwoDControllerThis controller type is designed to control a device capable of supplying 2D values. It has a very similar API to
CounterTimerControllerExample: a CCD
PseudoMotorControllerA controller designed to export virtual motors that represent a new view over the actual physical motors.
Example: A slit pseudo motor controller provides gap and offset virtual motors over the physical blades
PseudoCounterControllerA controller designed to export virtual counters that represent a new view over the actual physical counters/0Ds.
IORegisterControllerA controller designed to control hardware registers.
Controller plug-ins can be written in Python (and in the future in C++). Each controller code is basically a Python class that needs to obey a specific API.
Here is an a extract of the pertinent part of a Python motor controller code that is able to talk to a Newport motor controller:
from sardana.pool.controller import MotorController, \
Type, Description, DefaultValue
class NSC200Controller(MotorController):
"""This class is the Tango Sardana motor controller for the Newport NewStep
handheld motion controller NSC200.
This controller communicates through a Device Pool serial communication
channel."""
ctrl_properties = \
{ 'SerialCh' : { Type : str,
Description : 'Communication channel name for the serial line' },
'SwitchBox': { Type : bool,
Description : 'Using SwitchBox',
DefaultValue : False},
'ControllerNumber' : { Type : int,
Description : 'Controller number',
DefaultValue : 1 } }
def __init__(self, inst, props, *args, **kwargs):
MotorController.__init__(self, inst, props, *args, **kwargs)
self.serial = None
self.serial_state_event_id = -1
if self.SwitchBox:
self.MaxDevice = 8
def AddDevice(self, axis):
if axis > 1 and not self.SwitchBox:
raise Exception("Without using a Switchbox only axis 1 is allowed")
if self.SwitchBox:
self._setCommand("MX", axis)
def DeleteDevice(self, axis):
pass
_STATE_MAP = { NSC200.MOTOR_OFF : State.Off, NSC200.MOTOR_ON : State.On,
NSC200.MOTOR_MOVING : State.Moving }
def StateOne(self, axis):
if self.SwitchBox:
self._setCommand("MX", axis)
status = int(self._queryCommand("TS"))
status = self._STATE_MAP.get(status, State.Unknown)
register = int(self._queryCommand("PH"))
lower = int(NSC200.getLimitNegative(register))
upper = int(NSC200.getLimitPositive(register))
switchstate = 0
if lower == 1 and upper == 1: switchstate = 6
elif lower == 1: switchstate = 4
elif upper == 1: switchstate = 2
return status, "OK", switchstate
def ReadOne(self, axis):
try:
if self.SwitchBox:
self._setCommand("MX", axis)
return float(self._queryCommand("TP"))
except:
raise Exception("Error reading position, axis not available")
def PreStartOne(self, axis, pos):
return True
def StartOne(self, axis, pos):
if self.SwitchBox:
self._setCommand("MX", axis)
status = int(self._queryCommand("TS"))
if status == NSC200.MOTOR_OFF:
self._setCommand("MO","")
self._setCommand("PA", pos)
self._log.debug("[DONE] sending position")
def StartAll(self):
pass
def AbortOne(self, axis):
if self.SwitchBox:
self._setCommand("MX", axis)
self._setCommand("ST", "")
See also
- Writing controllers
How to write controller plug-ins in sardana
- Controller API reference
the controller API
Controllerthe controller tango device API
Footnotes