macroserver
MacroServer part of the kernel consist of one
MacroServer object which acts as:
container (inherits from
SardanaContainer) of:
macro parameter types managed by
TypeManagermacros managed by
MacroManagerobjects managed by
Poolinstances it is connected to (can be multiple of them)
facade (implements Facade pattern) to:
RecorderManager
The objects currently under MacroServer management are
communicated to the clients with the Elements attribute.
Door is just a thin layer in macro execution process
where the principal role plays MacroExecutor - one
instance per Door.
Macros are executed asynchronously using threads by one
ThreadPool with just one worker thread per
MacroExecutor.
Note
sardana-jupyter executes macros synchronously.
Macro execution consists of:
user inputs macro parameters
composing of XML document with macro execution information e.g. parameters parsing in Spock
execution of
RunMacro()command on Door Tango Deviceparameters decoding and validation by
MacroManagerandParamDecodercreation of macro object from its meta equivalent
MacroManagermacro execution using
MacroExecutor
Macro execution can be stopped, aborted or released, and the following sketch demonstrate different activity flows depending on where the macro was interrupted:
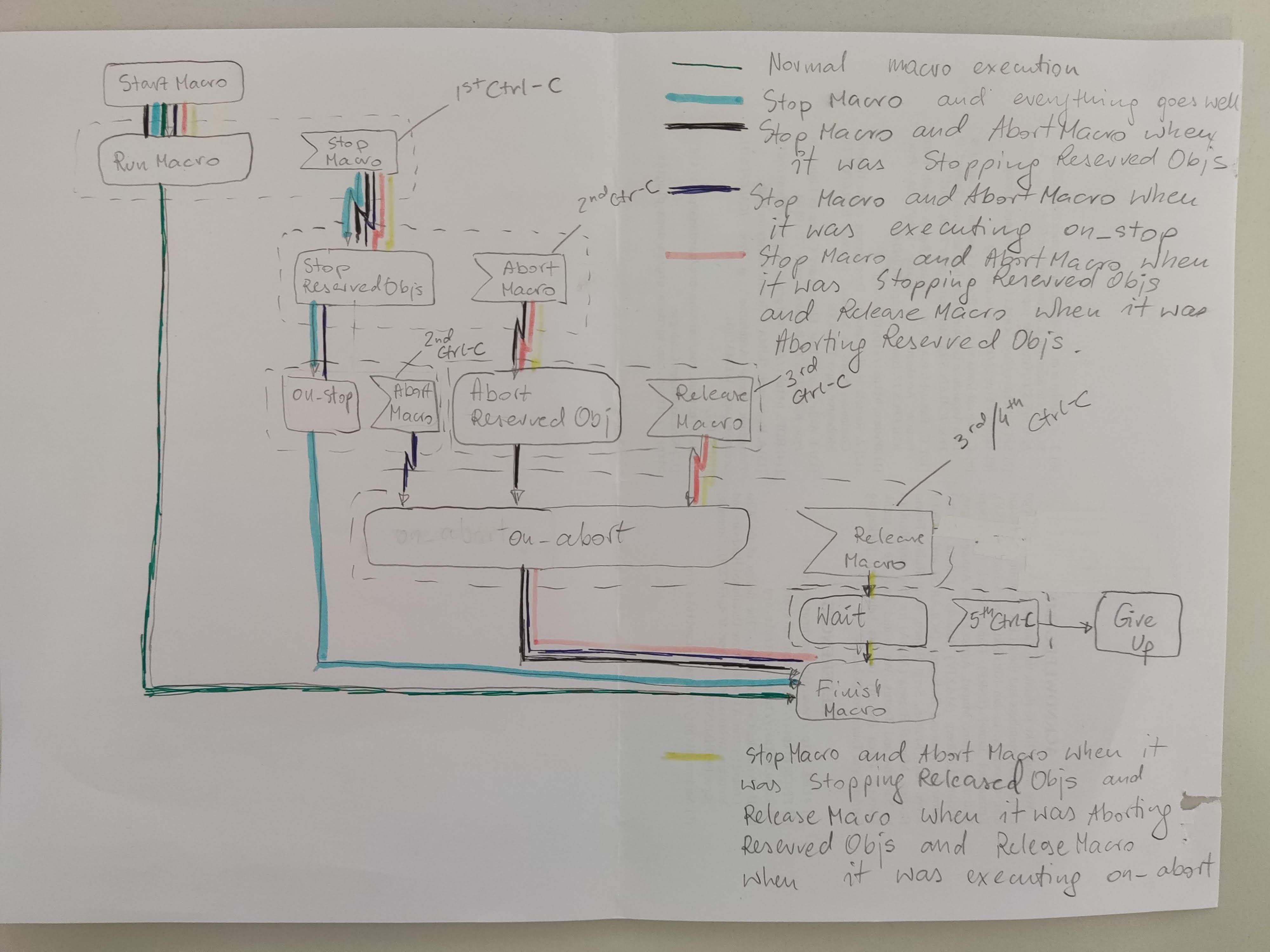
Activity diagram showing different execution flows of interrupting a macro
While Device Pool controllers are long-lived objects, recorders and macros are short-lived objects created on demand and destroyed when not needed anymore.
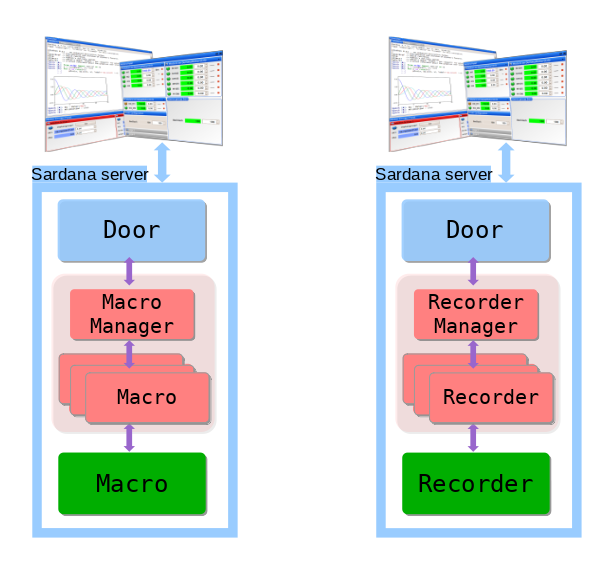
Main software layers of sardana on example of MacroServer macros and recorders
Modules